|
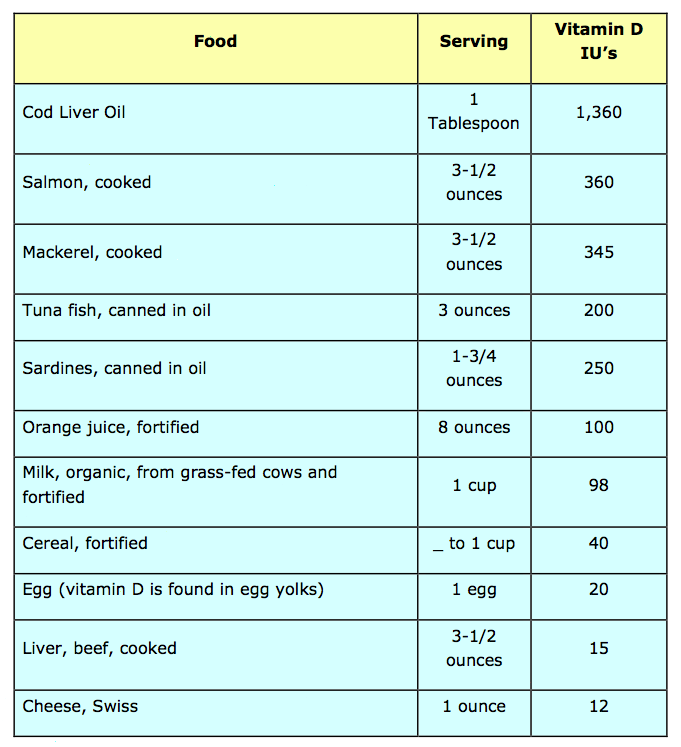
Sources of Vitamin D from Food
Sunshine is one of the best sources of Vitamin D. However, if you live more than 35˚ away from the equator there will be times between late fall and early spring where it won't be possible for you to produce the Vitamin D you need from the sun, so you have two alternatives: eat more vitamin D rich foods and/or take supplements. In this section, we discuss which foods provide the best source of vitamin D.
The following is a list of some of the foods that can increase your levels of vitamin D. Keep in mind, that ideally you should shoot for around 2,000 IU's
Good news if you don't like cod liver oil After sunlight, many people believe that one of the best natural sources of Vitamin D is cod liver oil. But for reasons that researchers do not understand, cod liver oil USED to be one of the best sources of Vitamin D. BUT the cod liver oil that is harvested today just simply does not have the amount of Vitamin D in it that your Grandma's cod liver oil did. So if someone is insisting you take it ... now you can tell them it not only tastes bad -- but it's not as good as other sources of vitamin D. Of course, that doesn't mean it isn't any good -- it just means that taking a supplements is probably the better choice. Personally, I prefer my IU's without the bad taste. Fish is Next Best As you can see from the list, one of the best food sources of Vitamin D come from fish Specifically, wild-harvested salmon and small fish like herring, sardines, and anchovies, and while tuna can provide some vitamin D – note that you should buy the tuna canned in oil (as Vitamin D is fat soluble). Stay away from the larger and farm-raised fish that are higher up on the food chain, as the mercury content may be too high to safely eat. Fortified Foods How much vitamin D is in fortified foods and supplements? Fortification of foods with vitamin D in the United States is carefully regulated. Vitamin D fortification is allowed for milk and milk products, cereal flours and related products, margarine, soy-based food products, and fruit juices and fruit juice drinks. Milk is usually fortified with 2.5 μg (100 IU) vitamin D per cup. Some yogurts are now fortified with vitamin D. Cheese, ice cream, and other dairy products made from milk are generally not fortified with vitamin D. To see if a food product has been fortified, check the food label. These days, most commercial milk suppliers fortify their products with vitamin D in the form of ergocalciferol (also known as D2) or cholecalciferol (D3). Some orange juice makers are doing the same, and like many food fads, you can soon expect to see lots of other products claiming to be good for you because they’re fortified with vitamin D. While the amount in these beverages is enough to ward off malnutrition, you’d have to drink gallons a day to reach optimal levels. That’s just too much milk or juice for most adults. But let’s not write off vitamin D-fortified foods altogether. A bakery in the US recently created a new vitamin D-fortified bread, but it contained so much vitamin D they had to go to Europe to test it, where allowable limits are more progressive. The recipe also included calcium carbonate, and the bread was reported to increase lumbar bone mineral density in the elderly patients consuming it. Fortified bread isn’t the way to go for everyone, of course, but it could provide a dietary option to weakly fortified milk and orange juice. Irradiated Mushrooms The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the USA has been seeking a natural, non-animal food, rich in Vitamin D. That led them to mushrooms. It has been demonstrated that when white button mushrooms are exposed to Ultraviolet B radiation, for a short period of time, the level of Vitamin D increases to levels many times the minimum daily requirement, i.e. 10 mcg. Normally, a serving of white button mushrooms contains 18 IU (0.45 mcg.). Treated mushrooms contain over 80 mcg. Mushrooms show great promise in becoming one of the best natural, non-animal sources of Vitamin D (great for Vegans). That being the case, there are some hurdles to overcome before Super-D Mushrooms are featured in the produce section of supermarkets. The hurdles involve not only production-line technology and shelf-life, but also bio-availability of the vitamin. These hurdles are being addressed in Canada, the USA and Australia – so ask about them when your next looking for produce. Note If you are a Vega ... or if you live in the UK and are looking for Vitamin D3 made from mushrooms - contact us as we just discovered and are going to try out a new source for these. We'll let you know where to get them. Conclusion In reality, it will be difficult to reach and sustain optimal levels of Vitamin D from dietary sources – especially in the winter months. Foods are a good source of Vitamin D - based on the government's recommended levels. This isn't to say you shouldn't eat any of the above foods, like most things when it comes to nutrition – a balanced approach is best: get some sun should continue to be your priority, eat right, and take supplements. So what do you do? Click here to find out.
Vitamin D is important for good health and long-life. Here are some of the articles we've added to our website to give you a full picture of this important subject. Like other parts of this website these articles summarize the important facts and include useful advice. If Vitamin D Were a Drug It Would Win the Nobel Prize Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes and Risk Factors Learn to recognize the symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, especially in women and children Testing Your Vitamin D Levels: (know what to ask your doctor, or order a home testing kit) Getting Vitamin D from Sunshine What you need to know when choosing a Vitamin D supplement Vitamin D Deficiency is linked to 2/3rds of the medical problems in the US along with poor diet Vitamin D helps prevent 3 out 4 cancers Vitamin D is Important for Good Heart Health Vitamin D and Calcium: You Need Them Both Vitamin D deficiency can cause mobility problems
The information contained in this section of our web site is for educational purposes and is not intended as medical advice. While the publishers of this website believe that people have the right to understand their own bodies and to take care of their bodies as they see fit, we also respect the knowledge and experience of trained nutritionists, scientists, researchers, medical practioners, and others who can help you achieve the optimum health you are entitled to, and suggest you seek out and work with health specialists you can trust. Back from this page on Sources of Vitamin D from Food to our lead page on Sunshine Vitamin D
|